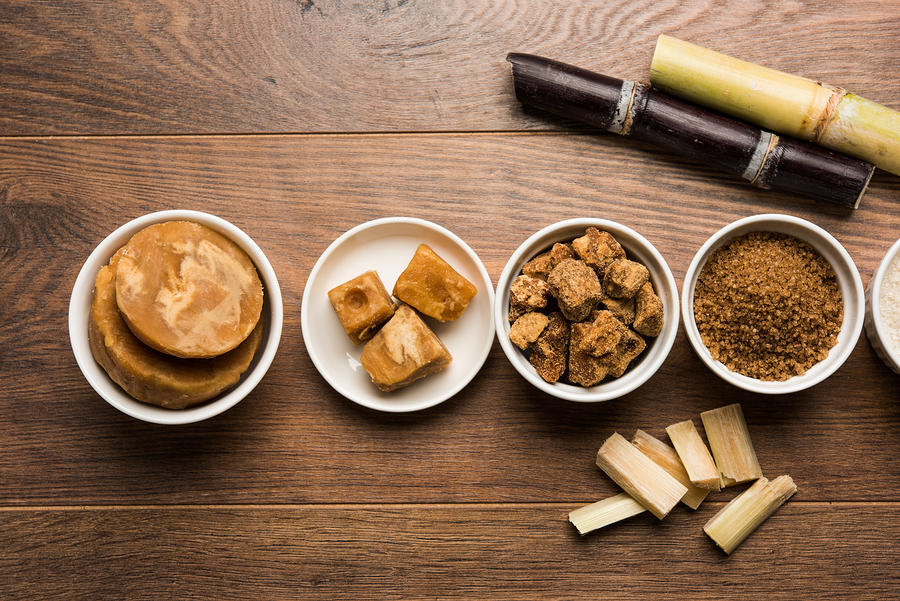
Palm sugar, derived from the sap of various palm trees, has gained popularity for its natural sweetness and potential health benefits. As consumers become more conscious about the environmental impact of their food choices, the sustainability of palm sugar has come under scrutiny. To understand its sustainability, it is crucial to differentiate palm sugar from the more widely known and controversial palm oil.
Table of Contents
Understanding Palm Sugar Production
Palm sugar is traditionally produced from the sap of the date palm, sugar palm, or coconut palm. The process begins with tapping the tree to collect the sap, which is then boiled and reduced to form a thick syrup. This syrup is further processed into granules, blocks, or liquid palm sugar. Unlike palm oil production, which involves large-scale deforestation and habitat destruction, palm sugar production tends to be more sustainable and less damaging to the environment.
Environmental Impact of Palm Sugar
Palm sugar production is often carried out by small-scale farmers using traditional methods. These practices usually involve minimal intervention in the natural ecosystem, allowing palm trees to coexist with other vegetation. Since palm trees can produce sap for many years, they do not need to be cut down after harvesting, unlike oil palm plantations which require replanting and often lead to deforestation.
Moreover, palm trees used for sugar production have a smaller ecological footprint compared to the oil palm. They grow well in diverse environments, including marginal lands that are not suitable for other types of agriculture. This adaptability helps in preserving natural forests and preventing further land conversion.
Economic and Social Benefits of Palm Oil
Palm sugar production provides a sustainable livelihood for many rural communities in tropical regions. It supports smallholder farmers, offering them a stable income and promoting economic development. Additionally, it encourages the maintenance of traditional agricultural practices, which can help preserve cultural heritage and biodiversity.
Misconceptions Linking Palm Sugar to Palm Oil
A significant challenge for palm sugar’s reputation is the frequent confusion with palm oil. Palm oil, extracted from the fruit of the oil palm, has been heavily criticized for its association with large-scale deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and human rights abuses. These issues have led to a negative perception of all palm-derived products, including palm sugar.
However, it is important to clarify that palm sugar and palm oil are distinct products with different production methods and environmental impacts. The problems associated with palm oil should not be generalized to palm sugar. Educating consumers about this distinction is crucial to ensure that sustainable products like palm sugar are not unfairly judged and can continue to provide benefits to communities and the environment.
Sustainable Palm Sugar Practices and Certification
To enhance the sustainability of palm sugar, several initiatives and certification programs are being implemented. Organizations are working to establish standards for sustainable palm sugar production, ensuring that it is environmentally friendly and socially responsible. Certification schemes, such as Fair Trade and organic labels, help consumers make informed choices and support ethical producers.
Palm Sugar In Summary
Palm sugar stands out as a sustainable alternative to conventional sweeteners, offering environmental, economic, and social benefits. Its production is less harmful to ecosystems and supports the livelihoods of small-scale farmers. However, it is essential to address the misconceptions linking palm sugar to palm oil and educate consumers about the distinct nature of these products. By promoting sustainable practices and supporting certification programs, we can ensure that palm sugar remains a viable and environmentally friendly option for the future.
Through informed choices and responsible consumption, we can enjoy the sweetness of palm sugar while contributing to a more sustainable and equitable world.




/https://public-media.si-cdn.com/filer/a0/c5/a0c5702e-acda-476b-95b5-fdd289df6003/vitamins.jpg)








